In the realm of digital marketing, search engine optimization (SEO) is often viewed as a multifaceted discipline, with various components working in harmony to improve a website’s visibility on search engines. Among these components, technical SEO stands out as a foundational pillar that addresses the backend aspects of a website. In this blog post, we’ll explore What is Technical SEO? A Complete Guide to understanding its importance, key components, best practices, and how to implement it effectively.
Understanding Technical SEO
Technical SEO refers to the optimization of a website’s architecture and infrastructure, ensuring that search engines can crawl, index, and understand your content effectively. Unlike on-page SEO, which focuses on content quality and keyword optimization, or off-page SEO, which revolves around link-building strategies, technical SEO addresses the technical aspects that make a website function optimally.
In this blog post, we’ll explore What is Technical SEO? A Complete Guide to enhancing the usability, speed, and overall experience of a website, not just for users but also for search engines. By ensuring that search engines can easily access and understand your website, you increase the likelihood of better rankings in search results.
The Importance of Technical SEO
- Search Engine Visibility: Technical SEO ensures that search engines can crawl and index your site effectively, allowing your pages to appear in search results.
- User Experience: A well-structured site improves user experience, leading to lower bounce rates and higher engagement. Happy users are more likely to convert into customers.
- Site Performance: Speed and performance are crucial. Slow-loading sites can lead to frustrated users, negatively impacting your rankings.
- Long-Term Benefits: Investing in technical SEO provides lasting benefits, helping your site adapt to algorithm changes and maintaining competitive positioning in search results.
Key Components of Technical SEO
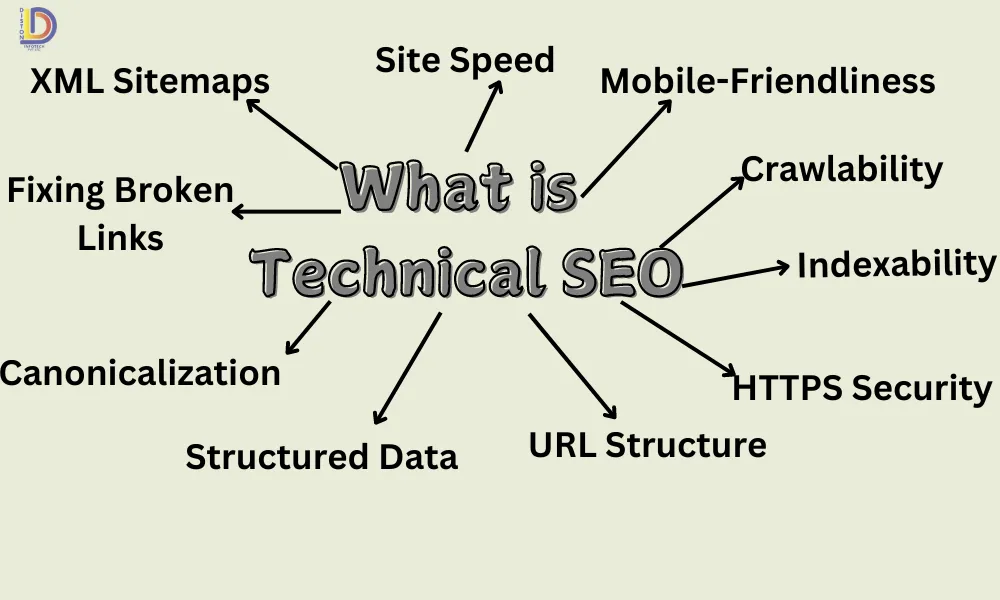
1. Site Speed
Site speed is a critical factor for both user experience and SEO. Websites that load slowly can deter visitors and lead to higher bounce rates. Google considers page speed as a ranking factor, so optimizing for speed is essential.
Best Practices:
- Image Optimization: Compress images without sacrificing quality.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Limit the number of elements on each page to reduce loading times.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Store certain elements on users’ devices to speed up loading on subsequent visits.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Distribute content across multiple servers globally for faster delivery.
2. Mobile-Friendliness
With the majority of web traffic coming from mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website is no longer optional. Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it predominantly uses the mobile version of your site for ranking and indexing.
Best Practices:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your website adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes.
- Touchscreen Readiness: Make buttons and links large enough to be easily clicked on mobile devices.
- Test Mobile Usability: Regularly check your site using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
3. Crawlability and Indexing
Crawlability refers to a search engine’s ability to discover and read your website’s pages. If search engines can’t crawl your site, they won’t index it, and it won’t show up in search results.
Best Practices:
- Robots.txt File: Use this file to guide search engines on which pages to crawl and which to avoid.
- XML Sitemap: Create and submit an XML sitemap to help search engines discover all your pages.
- Fix Broken Links: Regularly audit your site to identify and fix broken links, ensuring all pages are accessible.
4. Structured Data
Structured data, or schema markup, helps search engines understand the content of your site more accurately. This can lead to rich snippets, enhancing your search listings and potentially improving click-through rates.
Best Practices:
- Implement Schema Markup: Use relevant schema types for your content (e.g., articles, products, reviews).
- Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool: Validate your structured data to ensure it’s correctly implemented.
5. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Security is a significant factor in technical SEO. Websites using SSL (indicated by “https://”) are favored by Google. An SSL certificate protects user data and helps build trust with your audience.
Best Practices:
- Obtain an SSL Certificate: Make sure your website is secure by implementing HTTPS.
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure users are directed to the secure version of your site.
6. Canonical Tags
Duplicate content can confuse search engines, potentially diluting your rankings. Canonical tags help specify the preferred version of a webpage, guiding search engines to the right content.
Best Practices:
- Use Canonical Tags: Implement canonical tags on pages with similar content to indicate the original source.
- Audit for Duplicate Content: Regularly check for and resolve duplicate content issues.
7. 404 Pages and Redirects
404 errors occur when a page is not found, which can lead to a poor user experience. Setting up proper redirects is crucial for maintaining SEO value.
Best Practices:
- Custom 404 Pages: Create informative and user-friendly 404 pages that guide users back to relevant content.
- Implement 301 Redirects: Use 301 redirects to guide users and search engines from old URLs to new ones.
8. Internal Linking
A well-structured internal linking strategy helps search engines understand the hierarchy of your content and distributes page authority throughout your site.
Best Practices:
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Ensure anchor text is relevant to the linked content.
- Link Related Content: Encourage deeper exploration of your site by linking related articles and pages.
How to Conduct a Technical SEO Audit
Conducting a Technical SEO audit is a vital step in optimizing your site. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
Step 1: Crawl Your Site
Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to crawl your website. This will help you identify technical issues, including broken links, duplicate content, and missing meta tags.
Step 2: Check Site Speed
Utilize tools like Google Page Speed Insights or GTmetrix to analyze your site’s loading speed. Identify areas for improvement and implement the necessary changes.
Step 3: Review Mobile-Friendliness
Check your site’s mobile responsiveness using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. Make adjustments as needed to ensure a seamless experience for mobile users.
Step 4: Analyze Your URL Structure
Evaluate your URL structure for clarity and relevance. Make necessary changes to ensure that URLs are clean and descriptive.
Step 5: Optimize Your Robots.txt and XML Sitemap
Ensure that your robots.txt file is correctly configured, and that your XML sitemap is up-to-date. Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console for better indexing.
Step 6: Check for Security Issues
Verify that your site is served over HTTPS and that there are no security vulnerabilities. Regularly monitor for any potential threats.
Step 7: Monitor for Errors
Use Google Search Console to identify crawl errors, broken links, and other issues that may hinder your site’s performance.
Best Practices for Technical SEO
To stay ahead in the competitive world of SEO, consider the following best practices:
- Stay Updated: The SEO landscape is constantly changing. Stay informed about the latest trends, algorithm updates, and best practices to keep your site optimized.
- Prioritize User Experience: Always keep user experience at the forefront of your Technical SEO strategy. A well-structured, fast-loading, and secure site will lead to better engagement and conversion rates.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular Technical SEO audits to identify and address issues promptly. This proactive approach can prevent small issues from becoming major problems.
- Collaborate with Developers: If you’re not a technical expert, collaborate with developers to implement changes effectively. Clear communication between marketers and developers can lead to successful SEO strategies.
- Utilize SEO Tools: Leverage various SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz to gain insights into your site’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Technical SEO is an essential aspect of any comprehensive SEO strategy. By understanding what is technical SEO and optimizing the technical elements of your website, you not only improve its visibility in search engines but also enhance the overall user experience. In a digital landscape where competition is fierce, ensuring that your website is technically sound can make all the difference in achieving your marketing goals.
Investing time and resources into what is technical SEO pays off in the long run, helping your website adapt to changes and maintain a strong presence in search engine results. As you work on your SEO strategy, remember that technical SEO is the foundation upon which all other SEO efforts are built. Embrace it, and watch your online presence flourish.
Frequently Asked Questions About What is Technical SEO
1. What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the optimization of a website and server that helps search engine spiders crawl and index your site more effectively. It involves improving elements like site speed, mobile-friendliness, indexing, site architecture, and security to enhance search visibility.
2.Why is Technical SEO important?
Technical SEO is crucial because it helps search engines understand your website better, ensuring that your pages are indexed and ranking properly. A well-optimized site can lead to improved user experience, higher search rankings, and increased organic traffic.
3. What are some common Technical SEO practices?
Common Technical SEO practices include optimizing site speed, ensuring mobile responsiveness, creating an XML sitemap, using structured data markup, implementing HTTPS, fixing crawl errors, and optimizing URL structures.
4. How can I check if my site has Technical SEO issues?
You can use various tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog to analyze your website for Technical SEO issues. These tools can help identify problems such as broken links, slow page load times, and indexing issues.
5. What is the role of a robots.txt file in Technical SEO?
The robots.txt file is used to instruct search engine crawlers on which pages to crawl and which to avoid. Properly configuring this file is essential for controlling access to certain parts of your site and avoiding potential indexing issues.
6. How can HTTPS impact Technical SEO?
HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP and is important for Technical SEO because it encrypts data between the browser and the server. Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal, and having a secure site can build trust with users while improving your search ranking.
